Introducción
Se utiliza la librería de sympy para el análisis.
Descargar teoría PDF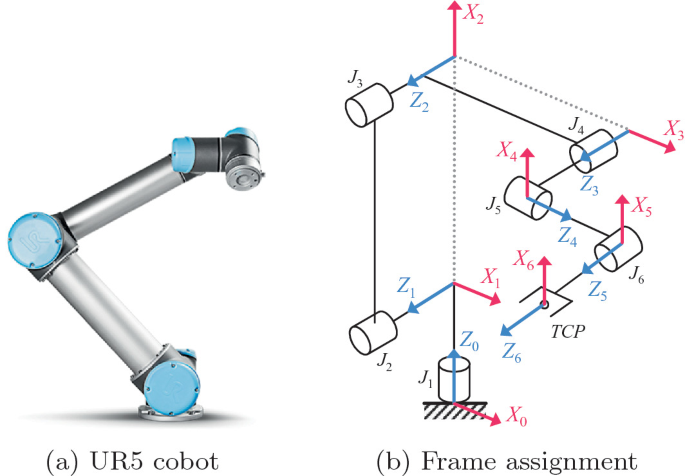
Se utiliza la librería de sympy para el análisis.
Descargar teoría PDF
import sympy as sp
# Variables
a1, a2, th1, th2 = sp.symbols('a1 a2 th1 th2')
m1, m2, g = sp.symbols('m1 m2 g')
th1_dot, th2_dot = sp.symbols('th1_dot th2_dot')
th1_dot_dot, th2_dot_dot = sp.symbols('th1_dot_dot th2_dot_dot')
# Posiciones
x_2=a1*sp.cos(th1)+a2*sp.cos(th1+th2)
y_2=a1*sp.sin(th1)+a2*sp.sin(th1+th2)
x_1=a1*sp.cos(th1)
y_1=a1*sp.sin(th1)
# Velocidades
print("\nVelocidades")
#Para V1
vx_1=a1*sp.cos(th1).diff(th1)
vy_1=a1*sp.sin(th1).diff(th1)
v1=sp.sqrt(vx_1**2+vy_1**2)
v1=v1.simplify()
print("Velocidad V1")
sp.pprint(v1)
#Para V2
#vx_2 y vy_2
#Matriz Jacobiana de velocidades
J=sp.Matrix([[x_2.diff(th1),x_2.diff(th2)],
[y_2.diff(th1),y_2.diff(th2)]])
#sp.pprint(J)
#Multiplicar por las velocidades angulares
Jv=J*sp.Matrix([th1_dot,th2_dot])
sp.pprint(Jv)
vx_2=Jv[0]
vy_2=Jv[1]
sp.pprint(vx_2)
sp.pprint(vy_2)
v2=sp.sqrt(vx_2**2+vy_2**2)
v2=v2.simplify()
print("Velocidad V2")
sp.pprint(v2)
#Energía cinética
print("\nEnergía cinética")
print("Para k1")
#Para V1
k1=0.5*m1*v1**2
sp.pprint(k1)
print("Para k2")
#Para V2
k2=0.5*m2*v2**2
sp.pprint(k2)
#Energía potencial
print("\nEnergía potencial")
print("Para P1")
#Para V1
p1=m1*g*y_1
sp.pprint(p1)
#Para V2
print("Para P2")
p2=m2*g*y_2
sp.pprint(p2)
L1=k1-p1
L2=k2-p2
L=L1+L2
print("\nLagrangiano")
L=L.simplify()
sp.pprint(L)
#Ecuaciones de Euler-Lagrange
#Para V1
d_part_L_th1_dot=L.diff(th1_dot)
d_part_L_th1_dot_dt=d_part_L_th1_dot.diff(th1)
d_part_L_th1=L.diff(th1)
eq1=d_part_L_th1_dot_dt-d_part_L_th1
#Reducir
eq1=eq1.simplify()
print("\nEcuación de Euler-Lagrange para t1")
sp.pprint(eq1)
#Para V2
d_part_L_th2_dot=L.diff(th2_dot)
d_part_L_th2_dot_dt=d_part_L_th2_dot.diff(th2)
d_part_L_th2=L.diff(th2)
eq2=d_part_L_th2_dot_dt-d_part_L_th2
#Reducir
eq2=eq2.simplify()
print("\nEcuación de Euler-Lagrange para t2")
sp.pprint(eq2)
╱ 2
╲╱ a₁
⎡-a₂⋅th_2_dot⋅sin(th₁ + th₂) + th₁_dot⋅(-a₁⋅sin(th₁) - a₂⋅sin(th₁ + th₂))⎤
⎢ ⎥
⎣ a₂⋅th_2_dot⋅cos(th₁ + th₂) + th₁_dot⋅(a₁⋅cos(th₁) + a₂⋅cos(th₁ + th₂)) ⎦
╱ 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2
╲╱ a₁ ⋅th_1_dot + 2⋅a₁⋅a₂⋅th_1_dot ⋅cos(th₂) + 2⋅a₁⋅a₂⋅th_1_dot⋅th_2_dot⋅cos(th₂) + a₂ ⋅th_1_dot + 2⋅a₂ ⋅th_1_dot⋅th_2_dot + a₂ ⋅th_2_dot
0.5⋅a₁ ⋅m₁
0.5⋅m₂⋅⎝a₁ ⋅th_1_dot + 2⋅a₁⋅a₂⋅th_1_dot ⋅cos(th₂) + 2⋅a₁⋅a₂⋅th_1_dot⋅th_2_dot⋅cos(th₂) + a₂ ⋅th_1_dot + 2⋅a₂ ⋅th_1_dot⋅th_2_dot + a₂ ⋅th_2_dot ⎠
a₁⋅g⋅m₁⋅sin(th₁)
g⋅m₂⋅(a₁⋅sin(th₁) + a₂⋅sin(th₁ + th₂))
0.5⋅a₁ ⋅m₁ - a₁⋅g⋅m₁⋅sin(th₁) - g⋅m₂⋅(a₁⋅sin(th₁) + a₂⋅sin(th₁ + th₂)) + 0.5⋅m₂⋅⎝a₁ ⋅th_1_dot + 2⋅a₁⋅a₂⋅th_1_dot ⋅cos(th₂) + 2⋅a₁⋅a₂⋅th_1_dot⋅th_2_dot⋅cos(th₂) + a₂ ⋅th_1_dot + 2⋅a₂ ⋅th_1_dot⋅th_2_dot + a₂ ⋅th_2_dot ⎠
g⋅(a₁⋅m₁⋅cos(th₁) + m₂⋅(a₁⋅cos(th₁) + a₂⋅cos(th₁ + th₂)))
a₂⋅m₂⋅(1.0⋅a₁⋅th_1_dot⋅(th_1_dot + th_2_dot)⋅sin(th₂) - 1.0⋅a₁⋅th_1_dot⋅sin(th₂) + g⋅cos(th₁ + th₂))